build_input¶
Module to create Input space and its child spaces from input data.
This module contains a function build_input(),
which creates “Input” space and its subspaces by reading
input data into them from an Excel file.
By default, build_input() reads data from input.xlsm in the
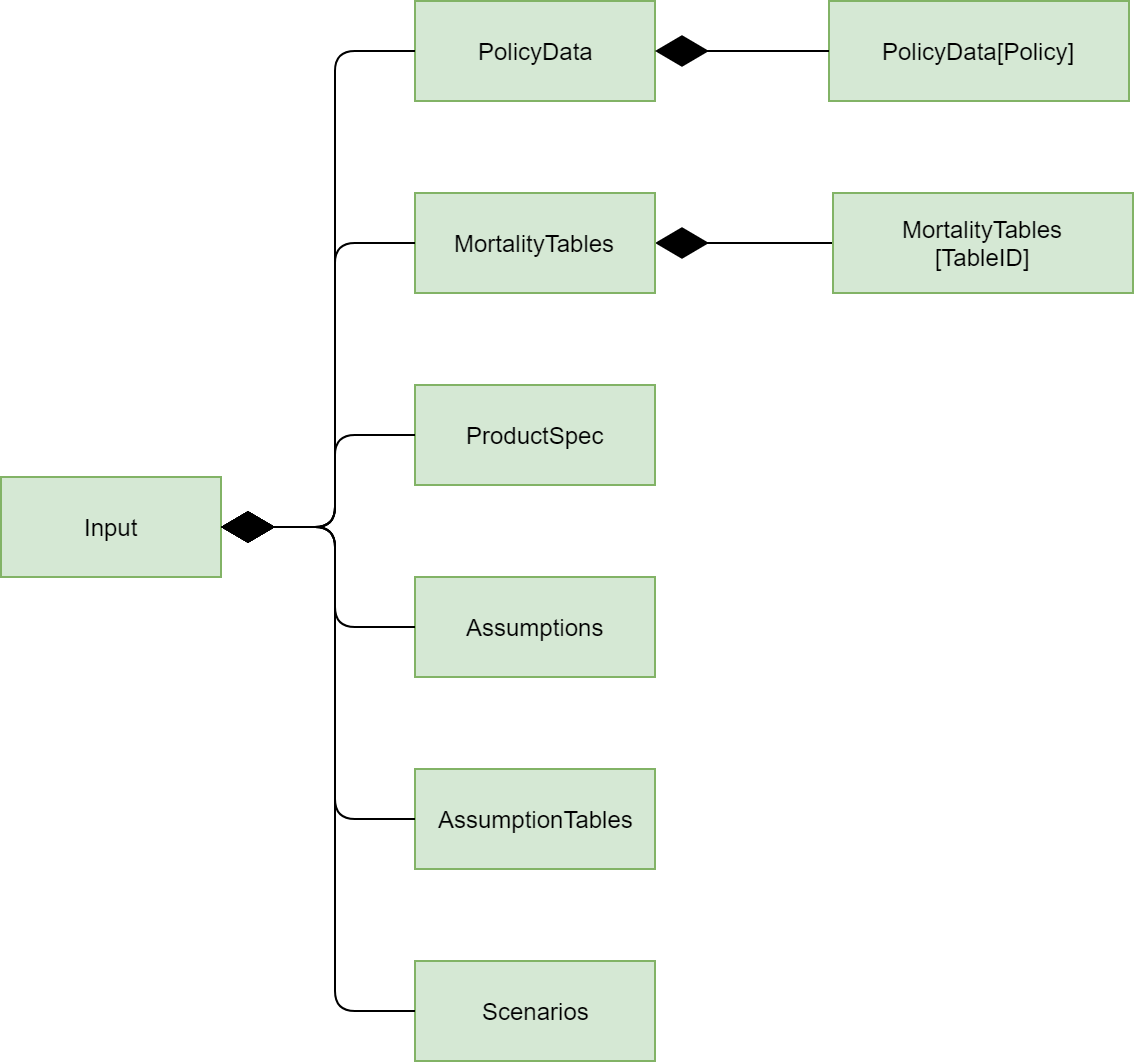
same folder as this module, and the structure of Input space is illustrated
by the diagram below.
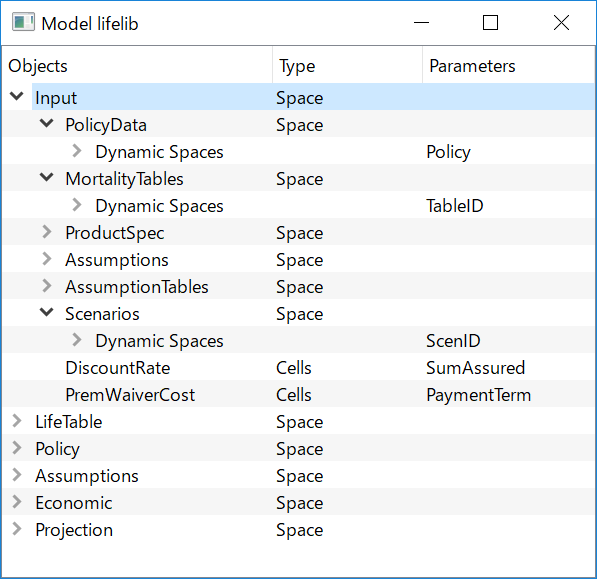
Below are descriptions of Input spaces and its subspaces.
- Input
The parent module of all other input spaces.
Some tables in input.xlsm are imported as cells directly under this space.
- PolicyData
The sample policy data read from PolicyData tab in input.xlsm. Records and fields of PolicyData represents policies and policy attributes respectively. Each record of PolicyData is accessible as a dynamic space under
PolicyDataspace indexed by Policy column in the input table. Each field of a record is accessible as a scalar cells in the dynamic space corresponding to the record.For example:
>>> model.Input.PolicyData[3].PolicyTerm()
gives the value of the policy term of the policy record 3.
- MortalityTables
The sample mortality tables read from Mortality tab. For Each mortality table, a dynamic space is created indexed by TableID, and MortalityTable cells indexed by
SexandAgeis created in that space.The script below will return the mortality rate of Male, Age 41 from the mortality table 3:
>>> model.Input.MortalityTables[3].MortalityTable('M', 41)
- ProductSpec
The sample product spec table read from ProductSpec tab.
ProductSpecdynamic subspaces holds parameters to specify products as cells. The dynamic subspaces are indexed byProduct,PolTypeandGen, and each of the subspace has scalar cells defined by the columns of ProductSpec tab other than the index columns.Empty cells in the index columns are imported as
None.Cells.matchmethod treatsNoneas the wildcard when finding the closest matching indexes for the given arguments.- Assumptions
The sample assumption table read from Assumptions tab.
The
Assumptionsspace has dynamic subspaces indexed byProduct,PolTypeandGen, each of which has scalar cells defined by the columns of Assumptions tab other than the index columns.Empty cells in the index columns are imported as
None.Cells.matchmethod treatsNoneas the wildcard when finding the closest matching indexes for the given arguments.- AssumptionTables
The sample assumption table read from AssumptionTables tab. The tab holds assumptions by policy duration, such as mortality factors and lapse assumptions.
Each assumption in the table is imported as a cells in the
AssumptionTablesspace.- Scenarios
- The sample scenario table read from Scenarios tab. TODO
Functions
build_input(model[, input_file]) |
Create “Input” space and its sub spaces by reading data from an Excel file into it. |
-
nestedlife.build_input.build_input(model, input_file='C:\\Users\\fumito\\Dropbox\\pyproj\\lifelib\\lifelib\\projects\\nestedlife\\input.xlsm')[source]¶ Create “Input” space and its sub spaces by reading data from an Excel file into it.
This function creates a space named “Input” under
model, reads tables frominput_fileinto cells and subspaces under the “Input” space.By default, this function assumes reading data from input.xlsm located in the same folder as this module.
Parameters: - model – Model object in which ‘Input’ space is created.
- input_file (str) – Path to the Excel input file.